|
Exploring Laminate: The Technical Side of Laminate Surfaces
Chances are, you encounter laminate hundreds of times in your daily life - perhaps without even realizing it. Laminate is found on kitchen countertops, in public bathroom partitions, in office cubicles and even on the table at your favourite restaurant. It may be one of the most functional and ubiquitous materials found in residential and commercial design. But despite its widespread use, few people understand exactly what laminate is, the different types or its many applications.
Laminate (commonly known as Laminex or Formica) benchtops have been around since the 1950′s. It is a hard-wearing, practical and very cost effective material, and it comes in a large range of colours (from solid colours to woodgrains, stone and abstract patterns). You can even get any image you desire printed as a laminate, and it is a popular choice for the budget conscious kitchen renovator.
What is Laminate?
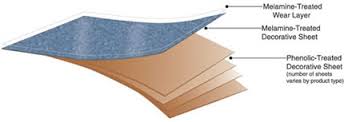
It is a man-made decorative material that is applied to the surface of a substrate. It is often referred to as HPL or high-pressure laminate, but its technical name is thermosetting high-pressure decorative plastic laminate. Laminate is available in hundreds of designs and it's low-maintenance, heat and impact-resistant properties, offer high value for the investment.
Laminate is manufactured one of two ways: under high pressure (HPL) or low pressure (LPL):
- HPLs are the most commonly used laminates. They are comprised of multiple layers of resin-treated paper fused together during manufacturing. HPLs can be adhered to a variety of substrates, have a dimensional behaviour similar to wood, and can expand and contract with humidity. They are recommended for any application in which durability and impact resistance are concerns, may be used for both vertical and horizontal surfaces, have a low initial cost and have a lifespan of five to 15 years. HPL is also available in hundreds of designs and multiple finishes.
- Low-pressure laminates (LPLs) are also known as melamine boards or direct-pressure laminates. They are comprised of a single-wear layer over a single decorative sheet, and are only recommended for vertical surfaces or low-impact/low-traffic areas. LPLs have a very low initial cost, but only a one to 5 year lifespan. They are available in a limited number of designs and finishes.
Designing With Laminate:
When selecting laminate for a project, there is more to consider than just colour and design. Designers must also make a decision on the type of laminate, texture, edge treatments and substrate or post forming needs. Most often, these decisions are based on performance needs, budget and intended use of the product.
Many people do not realize there are several types of HPL available. HPL is often divided into various product types: general purpose, vertical surface, postforming, flame retardant, high wear, cabinet liner and backers. Most laminate fall under the general-purpose category. General-purpose laminate can be used for both horizontal and vertical surfaces and in places where the surface must be functional, decorative and durable (such as a residential kitchen countertop or a work surface). Vertical-surface laminates provide a decorative and functional surface for walls or on surfaces that have minimal impact and wear. Post form-grade laminates are compatible with a heating and bending process that forms the laminate over a radius to eliminate seams.
More than 90 different types of specialty and performance laminates exist. Each one was developed to address specific performance needs, such as an extra-thick laminate that does not require a substrate, an extra-thin laminate used inside cabinets or a double-sided laminate that has a decorative face on both sides. Other specialty laminates were designed for specific environments, such as hospitals or buses. As the name implies; chemical-resistant laminate resists common chemicals. It may be used in hospitals, labs and other areas where a variety of chemicals or cleaning agents are used. Impact-resistant laminates contain a core made of aluminium or steel, and may be used in mass transit vehicles, light industrial facilities and maritime interiors. Wear-resistant laminates are produced for commercial, contract and institutional applications that demand a decorative surface, that can withstand more than normal wear. They have up to six times the abrasion and scuff resistance of conventional laminate. Another specialty laminate is fire-resistant laminate, which is produced for interior applications that require decorative surfaces with resistance to flames and smoke (in case of fire).
Once the type of laminate is selected, it is time to consider colour, design and texture. Most laminate companies have a standard offering of 200 to 250 design choices, and textured finishes add even more options. Some manufacturers have limited-access libraries of non-standard designs, including select discontinued patterns or custom patterns added for a large customer. These designs generally carry a longer lead time and premium up-charge. To add a custom design or colour for a client (outside the standard HPL offering), most manufacturers require a minimum annual usage of 250,000 square feet, and a three- to five-month lead time for the entire development process.
In addition to hundreds of colours and designs, laminate is also available in several textures. Most of these textures are created with stainless steel plates, but some specialty finishes require the use of textured foil. Finishes not only change the look of the laminate, but they can also affect how a laminate wears resistance, so the use and location of the laminate's texture should be considered when making a selection.
It is important to remember that when choosing a colour or texture, certain textures appear more scratch-resistant than others. For example, gloss textures show scratches more easily than matte textures. The more texture a surface has, the more it will resist scratching - texture can actually "interrupt" a scratch. Also, consider that certain colours and patterns minimize the appearance of normal wear. Scratches are less visible on light colours than on dark colours, and general wear and stains are less visible on patterns than on solid colours.
Always specify laminate under lighting conditions that match that of the final installation. While great care is taken in quality control of papers used in laminate production, some colours may have a metamerism.
Texture options include (this is only a small sample):
- Matte - A textured finish with a moderate reflective quality. Matte is the standard finish on most laminates.
- Crystal - A finely beaded design that minimizes fingerprints and has high scratch resistance.
- High Gloss - A texture with a mirror sheen finish that is susceptible to scratching and is not recommended for horizontal surfaces.
- Textured Gloss - A finish similar to waxed wood furniture.
- Beaded - A pebbled texture with the look and feel of coarse-grained sand.
- Woodgrain - An embossed finish with the look and feel of wood.
Installation Basics:
Laminate is only one of several raw materials used to build a finished product. Laminate must be bonded to a substrate, so adhesives, suitable substrates and backers are required for installation as well. Contact adhesives may be used for bonding laminates to a variety of cores. They are particularly useful for applications to metal or impervious surfaces. Contact adhesives should be uniformly applied to both surfaces that require bonding. These adhesives have high immediate bond strength, and once contact has been made, the components cannot be moved.
There are two primary types of adhesives: solvent-based and water-based. There are many different choices for a substrate, but the best choice is a substrate with high internal bond strength. Unsuitable substrates include plaster, plasterboard, gypsum board and concrete. A backer is then used to balance the laminate construction, prevent warping and protect the substrate from moisture. Backers are generally the same material as the top surface, or one matching in dimensional stability.
The process of heating the HPL to bend around a substrate form is called post forming. Most plastics once cured in manufacturing, cannot be reheated and reformed, but post forming laminate includes modified resins that allow the sheets to be reformed under heat and pressure. Once heated and formed, the laminate will hold its new shape permanently.
Post forming is used to create countertops, moldings, trim pieces and cabinet doors. It is helpful in places where a "solid" or seamless look is preferred (such as deck edges and cabinet doors), or where "kid-friendly" curves are welcome, since they eliminate sharp edges. Post forming is also used to achieve special edge treatments, laminate inlays or inlays with other materials such as tile, wood or metal.
Uses for Laminate:
Some of the most common and recognizable uses of laminate include residential countertops and cabinetry, office work areas, public restrooms and department store wall panels. Laminate is also abundant in corporate offices, retail stores and malls, hospitality environments, healthcare settings and educational institutions.
It should not be used in areas with extremely high moisture, humidity, extreme heat or cold, in aseptic rooms or outdoors.
Laminate Uncovered:
Once you know what to look for, you will notice that laminate is everywhere. If you look around your office, you may see laminate in cubicles, on the reception desk, in restrooms, on the conference table, on the elevator control panel or even within some of your office furniture. The material is very durable, extremely functional and highly fashionable. Now that you know the technical side, we hope you realize it is an extremely versatile and usable material as well.
Laminate - it's not just for kitchen countertops anymore.
For laminate bench top 'fact sheet 101', click here.
For care and maintenance information about Laminate bench tops, click here.
For laminate bench top Tips and Design Advice, click here.
We hope that this information has been helpful for you.
If you need further help or more information on this topic please:
|